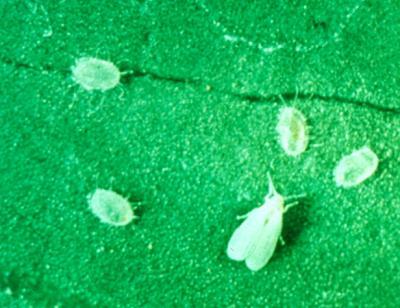
Vegetable
Severe infestation may cause plant damage such as mottling and yellowing of leaves as well as a reduction of vegetable yields. Whitefly (covered by a white waxy powder) adults are small "dandruff" size insects. When plants are disturbed, the whiteflies flutter around the plant and soon return to the plant to continue feeding.
On indoor plants one can try using yellow sticky traps to capture the adults. These work much better if the foliage is disturbed daily, causing the whiteflies to fly off of the plant. Infestations can also be reduced by discarding heavily infested plants.
Outdoors, use suggested insecticides according to all label directions and precautions. Insecticidal soap, summer oil, and chemical insecticides are effective.
On vegetables, be sure to follow the recommended time interval between treating the plants and harvesting the crop. If there is no pre-harvest interval,DO NOT use that insecticide on the food crop.