|

Plant Parts - Fruit
The fruit is the ripened ovary of a plant containing the
seeds. After fertilization,
the ovary swells and becomes either fleshy or hard and dry
to protect the developing seeds. Many fruits help seeds
spread (maple seeds). Many things we call vegetables are
really fruits such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and beans.

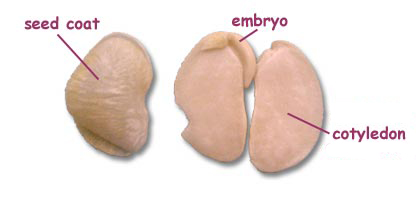
Every seed is a tiny plant (embryo)
with leaves, stems, and root parts waiting for the right
things to happen to make it germinate and grow. Seeds are
protected by a coat. This coat can be thin or thick and
hard. Thin coats don't protect the embryo well. But thick
coats can let the embryo survive some tough conditions.
The seed also contains a short-term food supply called
the endosperm
which is formed at fertilization but is not part of the
embryo. It is used by the embryo to help its growth. In
the bean that is shown, the endosperm is no longer there.
It has been used for the growth of the embryo, and most
of its nutrients and energy are now in a different form
within the tissues of the cotyledon.
Plants with one cotyledon (like corn) are called monocots.
If they have two cotyledons (like beans), they are called dicots.
Seeds are a plant's way of getting from one area to another by either wind, water or animals.
|



